How much is Google’s bot detection really worth?
An analysis of how well reCAPTCHA detects bots.
Last updated: July 2nd, 2025
Intro
For more than a decade, Google's reCAPTCHA service has offered website owners a trade: let Google track your users and ask them questions, and in exchange they promise to stop bots and spam.
More than 4.5 million websites use reCAPTCHA [1] and the system collects hundreds of millions of daily solves. [2] This equates to more than 100 person-years of labor every day.[ 3]
Labeled data is the fuel that powers machine learning. reCAPTCHA answers have been used to improve Google's ML/AI services since 2009. Many people who use reCAPTCHA don't realize their labor is being put to use.
Google is now charging high prices for reCAPTCHA Enterprise, causing many companies to reevaluate this deal.
Major companies like Shopify and many others have switched to hCaptcha's enterprise solutions in response.
As of January 2024, Google has increased prices again on reCAPTCHA, nearly eliminating the free tier. They have also announced that all reCAPTCHA keys must move to a Google Cloud account in 2025.
This means hCaptcha Enterprise has both better detection, a much more comprehensive feature offering, and dramatically better ROI.
Is this a fair trade?
The hCaptcha team has been collecting pricing data from "dark web" captcha-breaking services since 2016. We noticed an interesting trend:
The average cost of breaking a reCAPTCHA is incredibly low (less than $1 per 1000 solves) and has not materially increased since our monitoring began in 2016. This applies to both reCAPTCHA v2 and v3. [4]
Pricing data lets us put an exact dollar value on the security offered by a reCAPTCHA: $0.001 or less per answer.
Google charges $1 per 1000 requests or more for reCAPTCHA Enterprise, meaning they now charge more per request than it costs to break the security of their service. This seems like a bad deal.
By contrast, no major dark web solver services currently support hCaptcha, due to hCaptcha's more advanced challenges and more aggressive anti-crime strategic approach.
What else is Google doing with your data?
Google has spent more than two decades attempting to combine data from across its many services in order to sell you ads. As an ad company, this is always their ultimate goal: Google generates the vast majority of their revenue from advertising.
Even when Google explicitly says they're not collecting data, they sometimes are forced to later admit that they are, for example using their Streetview cars to collect Wi-Fi data from home networks.
And when they claim they are not using data, it often seems to be on a technicality. For example, they have published work on "privacy-preserving" systems that just barely anonymize data in a way that is very easy to undo. This is not surprising: anything that prevents their ad profiling models from constructing an accurate view of your interests is unlikely to see the light of day at Google.
Despite increasingly strict data privacy laws around the world, it is probably safe to assume that they continue to use as much of your data as they can get to better sell you ads.
Is Google's reCAPTCHA service GDPR compliant?
Probably not:
The French data protection authority, the CNIL, has ruled that reCAPTCHA uses excessive personal data for purposes other than security, harming the privacy of people who use online services that embed reCAPTCHA.
By contrast, hCaptcha does not sell ads, and we have no use for user information other than to provide security services.
This is why we have launched unique hCaptcha Enterprise features like our Zero PII offering, letting sites completely blind user data before we ever see it. Aggressive data minimization through sampling, blinding, and the minimum practical retention periods has been our principle since day one.
Is there an alternative to this unfair deal?
hCaptcha is the first credible alternative, now used by hundreds of millions of people each month.
As users prove their humanity via hCaptcha, their labor enters an anonymous open market for bidding.
Companies all over the world bid for that labor to complete simple tasks that are easy for people but hard for machines. Users support the site they are visiting, and experience less web spam due to a higher level of security.
hCaptcha Enterprise customers gain total control over the experience, and benefit from the expertise hCaptcha has gained operating the largest independent challenge provider on the internet. They also get a better deal than reCAPTCHA Enterprise: up to 50% better pricing, depending on volume.
The wide and often-changing variety of tasks on hCaptcha are also harder to automate. reCAPTCHA's single interface has not changed in many years, and has a small set of infrequently changing questions. This is one of the ways hCaptcha provides more robust anti-bot protection than reCAPTCHA.
hCaptcha uses advanced machine learning to deliver what reCAPTCHA only promises, and the ROI is obvious.
Users know their data isn't being sent to an ad company, and experience less web spam. This seems like a fairer deal.
Why hasn't reCAPTCHA improved over time?
There has been a revolution in deep learning since 2012. The industry norm for task accuracy has radically improved over the past decade, primarily due to deep convolutional networks. Other ML-powered services Google offers have followed this curve.
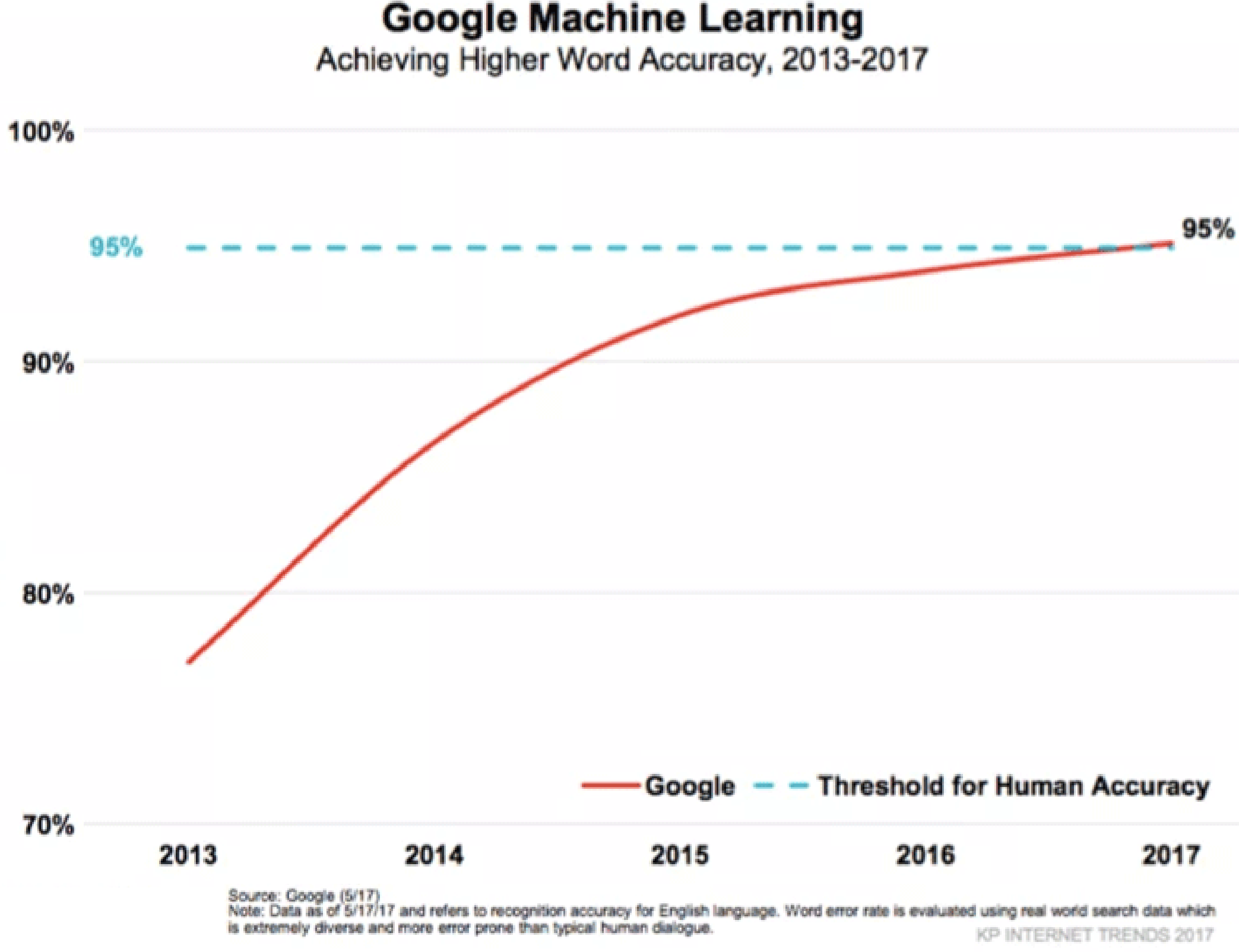
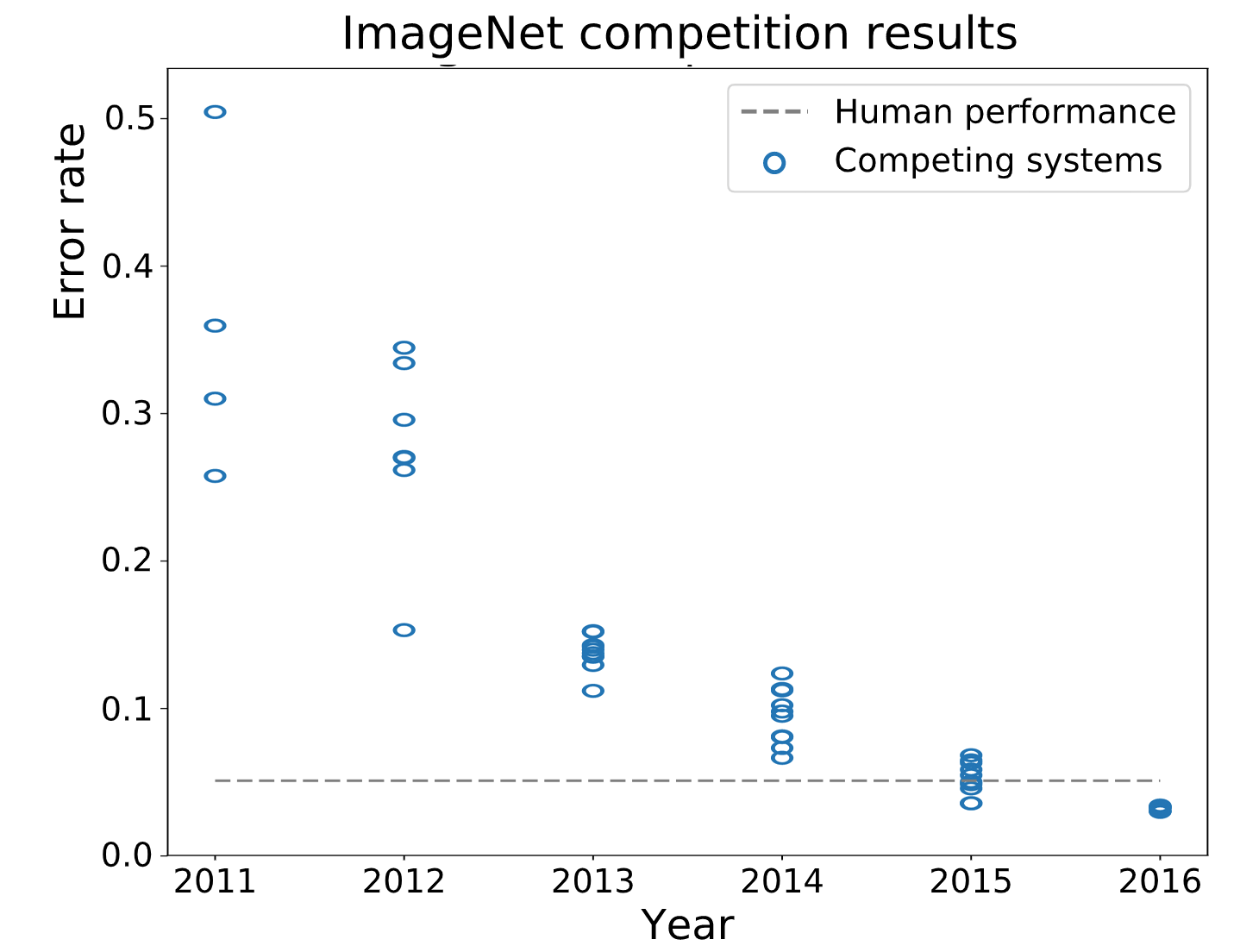
(See footnotes 6 and 7.)
ML has improved, but the difficulty of bypassing reCAPTCHA has not materially changed during this time.
Improving reCAPTCHA creates an intrinsic conflict for Google as an ad vendor.
Every bot identified by reCAPTCHA directly reduces Google's ad revenue.
If Google itself determines that a user seeing an ad or clicking a link was in fact a bot, it cannot charge for ads shown to that user. This conflict of interest has severely limited the scope of Google's anti-bot ambitions.
For example, Google has not offered obviously valuable services like retroactive bot detection. It is much more reliable to declare user traffic bot-generated after analyzing several days of data.
Knowing after the captcha that some users were bots is also valuable. It lets website owners clean out old spam posts and delete "sleeper accounts" registered to spam forums in the future, reduce fraud, and more.
Offering retroactive bot identification would open Google up to thorny questions of how to retroactively refund advertisers who spent money on that fraudulent traffic.
The reCAPTCHA product has thus stagnated for a decade.
Users have suffered, and unnecessary web spam is now rampant. But there is an alternative.
How is hCaptcha different?
hCaptcha is the only major captcha service not owned by an ad network.
hCaptcha's incentive is to maximize accuracy, not ad revenue: bot answers are useless for our customers, who need human training data.
hCaptcha cares about privacy, transparency, and fairness.
Knowing who an individual is has minimal value for hCaptcha. We only care whether they are human or a malicious actor.
hCaptcha shares the value of work done while users prove their humanity.
Instead of offering a service of questionable value while extracting labor with real value, hCaptcha provides both compensation and strong anti-bot protection.
hCaptcha offers a fair deal to both free and enterprise (hCaptcha Enterprise) customers.
Instead of offering an easily defeated service to free users while charging millions of dollars for an enterprise version that is not much better, hCaptcha provides excellent bot protection to both, while offering enterprise users additional features and customization, along with strong SLAs and rapid support.
Who built hCaptcha?
hCaptcha is a service of Intuition Machines (imachines.com), a machine learning company that offers products and services for companies implementing machine learning at scale.
The IM team is composed of scientists and engineers from Apple, Amazon, and other leaders in machine learning, distributed systems, and security.
IM scientists regularly publish in top conferences like ICML, ICLR, ECCV, and NeurIPS, and the company has publicly released state-of-the-art results in ML disciplines like deep hashing [8][9] and OCR [11].
What kinds of challenges run on hCaptcha?
hCaptcha supports a wide variety of challenges.
Below are two examples. [10]
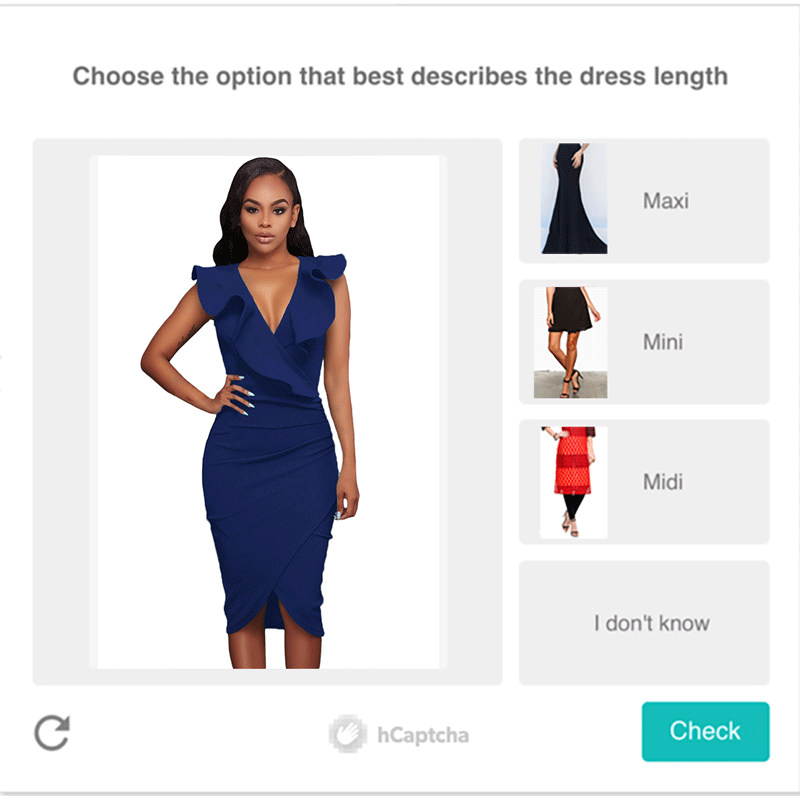
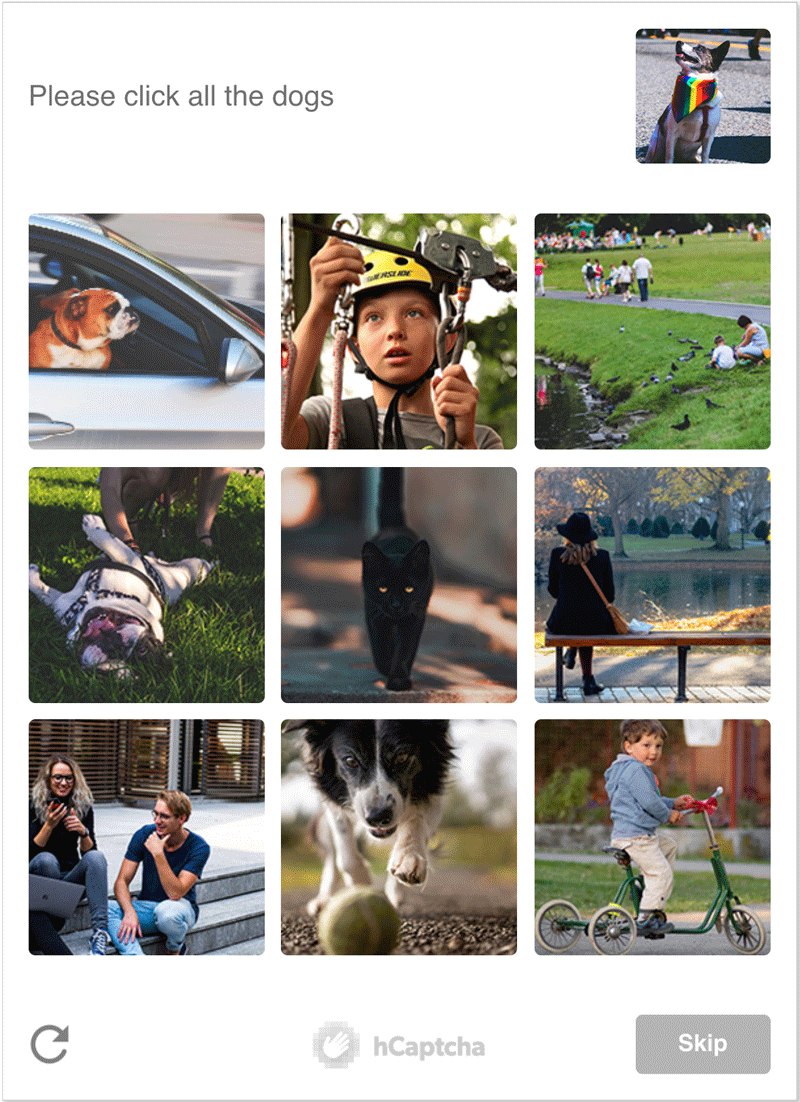
Who are hCaptcha's paying customers?
hCaptcha customers span a variety of industries, from technology companies to those focused on fashion, retail, and other areas where their online services see fraud or abuse.
hCaptcha is committed to democratizing access to world class security services, letting companies big and small improve the quality of their products and services by applying security-focused machine learning to their business.
Questions?
We take your feedback seriously, and want to ensure everyone has a more pleasant experience online, with fewer bots and less spam. Reach out to us: support@hcaptcha.com.
And if you think the cost of reCAPTCHA is too high, ask us about hCaptcha Enterprise. Currently in use by some of the largest publishers, financial services companies, and web infrastructure companies in the world, this is not only a credible alternative to reCAPTCHA: we believe it offers the best bot protection and human abuse defense currently available.
Footnotes
1. Source: BuiltWith.com reCAPTCHA site listings. Retrieved July 9th, 2019.
2. https://developers.google.com/recaptcha/ ("Hundreds of millions of CAPTCHAs are solved by people every day.") Retrieved July 8th, 2019.
3. Conservative estimate: 200 million solves * 30 seconds per solve in years = 190.3 person-years/day.
4. hCaptcha internal analysis. Data harvested through June 30th, 2019. Details available upon request.
5. Conservative estimate: $0.01 cost of a single annotation * 200M avg. annotations per day (lower bound) * 365 days per year * 10 years since 2009 acquisition = $7.3 billion lower bound value.
6. Credit: Gkrusze [CC BY-SA 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)]
7. Source: Mary Meeker, KP Internet Trends 2017
8. https://lld-workshop.github.io SEMANTIC HIERARCHY BASED RELATIONAL EMBEDDINGS FOR WEAKLY-SUPERVISED DEEP HASHING, Heikki Arponen, Tom E Bishop. ICML 2019, LLD Workshop.
9. https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJgqFi5rOV Recent state-of-the-art results: ICML LLD, May 2019.
10. Royalty-free example images. Source: Petapixel.
11. IM Scientists Set New Benchmark for Weakly Supervised Text Recognition (OCR) at CVPR 2020.
Trademark notes:
"Intuition Machines" is a registered trademark of Intuition Machines, Inc.
All product names, logos, brands, trademarks and registered trademarks are property of their respective owners. All company, product and service names used in this website are for identification purposes only. Use of these names, trademarks and brands does not imply endorsement. In this case, quite the opposite.